Monant Medical Misinformation Dataset: Mapping Articles to Fact-Checked Claims
Srba, I., Pecher, B., Tomlein, M., Moro, R., Stefancova, E., Simko, J., Bielikova, M. – SIGIR ’22, 2022
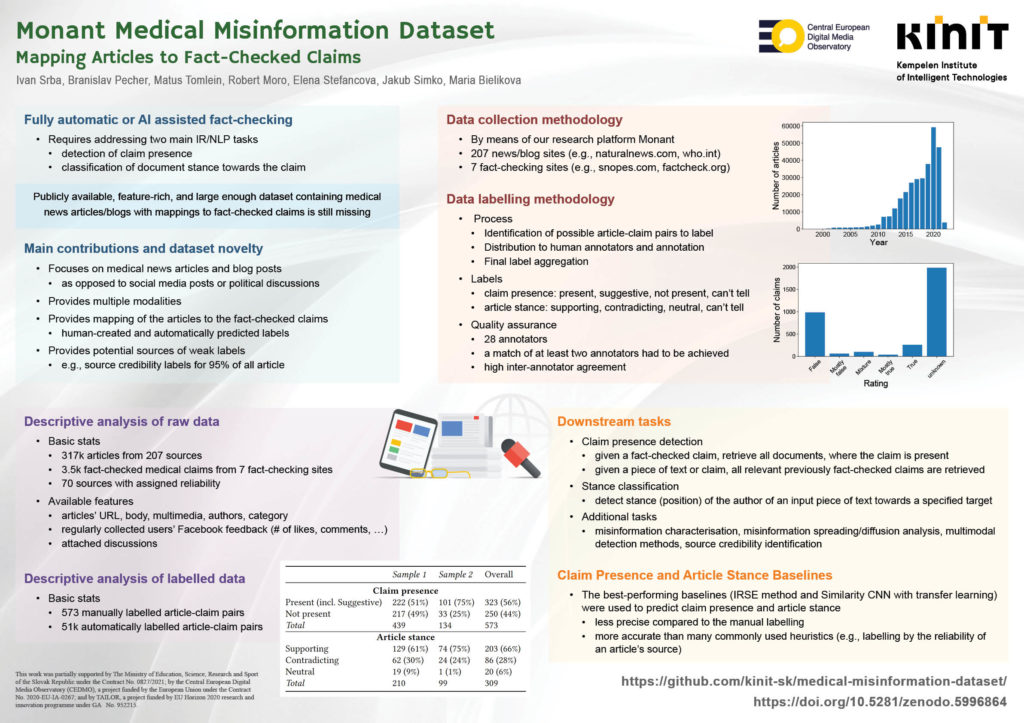
False information has a significant negative influence on individuals as well as on the whole society. Especially in the current COVID-19 era, we witness an unprecedented growth of medical misinformation. To help tackle this problem with machine learning approaches, we are publishing a feature-rich dataset of approx. 317k medical news articles/blogs and 3.5k fact-checked claims. It also contains 573 manually and more than 51k automatically labelled mappings between claims and articles. Mappings consist of claim presence, i.e., whether a claim is contained in a given article, and article stance towards the claim. We provide several baselines for these two tasks and evaluate them on the manually labelled part of the dataset. The dataset enables a number of additional tasks related to medical misinformation, such as misinformation characterisation studies or studies of misinformation diffusion between sources.
Cite: Ivan Srba, Branislav Pecher, Matus Tomlein, Robert Moro, Elena Stefancova, Jakub Simko, and Maria Bielikova. 2022. Monant Medical Misinformation Dataset: Mapping Articles to Fact-Checked Claims. In Proceedings of the 45th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval (SIGIR ’22), July 11–15, 2022, Madrid, Spain. ACM, New York, NY, USA, 11 pages. DOI: 10.1145/3477495.3531726
The source code and dataset sample is available at Github
The full dataset is available at Zenodo